If you have wondered what the numbers 192.168.203.1 on the back of your wireless router mean – these are your device’s default private IP address. To manage traffic and prioritize your network usage, you can configure IP QoS (Quality of Service) settings at this address. Assigned by the router’s manufacturer, the default IP address is the backbone of your WiFi, used to establish a connection between all gadgets you connect to the network. The 192.168.203.1 IP address is also where you go to access your router’s admin panel, where you can manage network priorities using IP QoS (Quality of Service) settings, improve the security of the wireless, enable built-in features such as a firewall and VPN, and much more. You can also change the router’s default IP address at any time you’d like.
How to Get into The Admin Menu of your 192.168.203.1 router
Your router’s local IP address can be easily found in one of three places:
- The user manual that came with the device
- The manufacturer’s website, after searching for the exact model
- The label at the back of the device itself.
Once you made sure that 192.168.203.1 is indeed the private IP address your router is using, you can proceed to typing it into the address bar of the browser you are using. Make sure to use the default username provided by the manufacturer for the first login. Just make sure that you are connected to the WiFi, or directly to the router via an Ethernet cable first. The username and password you should use to access the menu will be listed in the same places that as the 192.168.203.1 private IP.
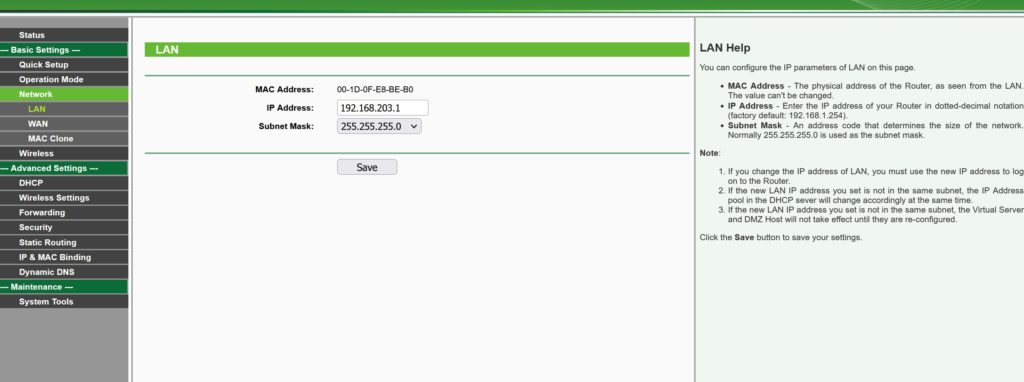
How to Change Your Private IP to 192.168.203.1
If you’d like to change the private IP address that your router uses from the default one to 192.168.203.1 (or vice versa), you can easily do that from the admin menu you just gained access to. When changing the WiFi password, ensure it’s complex to prevent unauthorized access. To do that, simply log into the admin panel at 192.168.203.1 (or your current private IP) and look for the Network Settings tab. There you will see the IP currently in use listed, as well as the option to change it. You can update it to 192.168.203.1 and hit save. Just remember that the next time you try to log into the admin menu, you will need to use that default IP address.
Update your SSID at 192.168.203.1
The Service Set Identifier (SSID) makes your wireless network stand out among other networks within wireless range. The name of your network can be something personal to you, or if you are using your 192.168.203.1 router at the office, a professional designation – the name of your company, or your department. To improve security, change wifi password regularly in the admin panel. In any case, it would be a good idea to change the SSID from the default one, which is usually the brand and model of your router. This should be done for security reasons as well because potential hackers will have a harder time accessing your WiFi settings when you do that.
Set Up a Secure Password for your WiFi
You should definitely make sure to set up a secure, hard-go-guess password that you and other members of your network are going to use to log onto your WiFi. A strong password serves as the first line of defense against network intrusions. You can do that in the same sub-menu that you went to update your network’s SSID. Once you click on the Wireless Settings tab, go to the SSID field, and you will find the password right beneath it. Most routers require a password of at least 8 characters, but using at least 12 is the common advice. It is advisable to use a mix of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols for your password. Make sure to remember your new password, because you will need it to log onto your WiFi after you hit Save.
Fix Potential Issues with your Router’s Connection
It is possible that you try connecting to your router at 192.168.203.1, or browse the internet, and get a Connection error message. If you encounter a proxy error, verify the proxy settings in your browser to ensure they’re configured correctly for your network. The first thing to do in such a case is to see if the lights on the front of the router are on and green. You might want to double-check the LAN cable connection as well. Restarting the device by plugging off the power cord for 15 seconds and plugging it back in is the most commonly used method for fixing the Connection Error message. It works 90 percent of the time. If the issue persists after that, consider giving your ISP a call.
Troubleshooting connectivity problems with a router using the IP address 192.168.203.1 requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve the issues effectively. Here are some steps to help you diagnose and fix the problem:
- Physical Checks: Begin by inspecting the physical connections. Ensure that all cables are securely plugged into your wireless router and connected devices. Look for any visible damage to cables or ports.
- Power Cycle: Often, a simple power cycle can resolve minor issues. Turn off the router, wait for 30 seconds, and then turn it back on. Allow it a few minutes to initialize.
- Check IP Configuration: Ensure that your device is set to obtain an IP address automatically (DHCP). Incorrect static IP settings can lead to connectivity problems.
- Ping Your Network Router: Open the command prompt or terminal on your device and ping the router’s IP address (ping 192.168.203.1). If you receive responses, it indicates a connection to the router.
- Check for Firmware Updates: Outdated router firmware can cause issues. Visit the router manufacturer’s website to check for firmware updates and apply them if available.
- Reset Your Router: If the problems persist, you may need to reset your router to its default settings. Be cautious, as this will erase all custom configurations.
- Firewall and Security Software: Disable or adjust firewall and security software settings on your computer, as they may block router communication.
- Interference: Check for interference from other electronic devices and Wi-Fi networks in your vicinity. Adjust the router’s channel settings if needed.
- Contact Your ISP: If none of the above steps work, the issue might be with your internet service provider. Contact them to check for any service outages or issues on their end.
